Introduction
Nigeria, Africa’s largest economy, has emerged as a leading hub for technology startups, driving innovation and attracting both local and foreign investment. The rise of these tech companies not only marks a significant shift in the economic landscape but also signals the potential for profound socio-economic transformation. This article aims to explore the extent of the impact that these startups have on Nigeria’s economy, focusing on areas such as job creation, GDP contribution, and technological advancement.
Recent Trends in Tech Startups
Growth of the Sector
Over the last decade, Nigeria has seen an exponential increase in the number of technology startups. This growth is primarily fueled by the youthful demographic, with over 62% of the population under the age of 25 and a high rate of tech literacy among young adults. Startups in Nigeria are not just proliferating; they are increasingly successful in securing substantial investment rounds. For instance, Nigerian startups raised over $1.8 billion in funding in 2021 alone, accounting for 35% of the total African tech startup funding for that year.
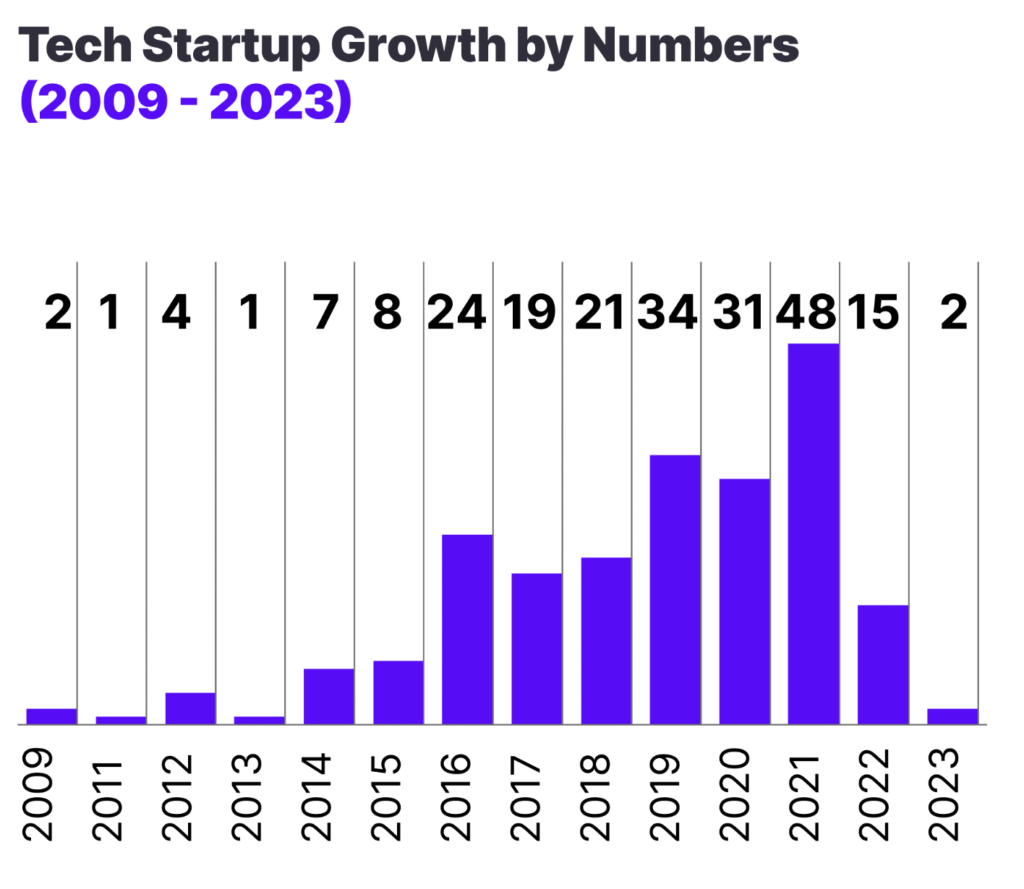
Major Areas of Focus
The landscape of Nigerian tech startups is diverse, but certain sectors stand out due to their rapid growth and investment attraction:
Fintech: Financial technology firms lead in terms of numbers and funding. Companies like Paystack and Flutterwave have revolutionized payment systems in Nigeria and across Africa, facilitating smoother transactions in a continent traditionally dominated by cash.
Healthtech: Startups in the health sector are addressing significant gaps in medical services, offering solutions from telemedicine to health data analytics, thus increasing access to healthcare for underserved populations.
Agritech: Agriculture remains a cornerstone of the Nigerian economy, and tech startups in this sector are innovating ways to boost agricultural productivity and supply chain management, benefiting smallholder farmers and the economy at large.
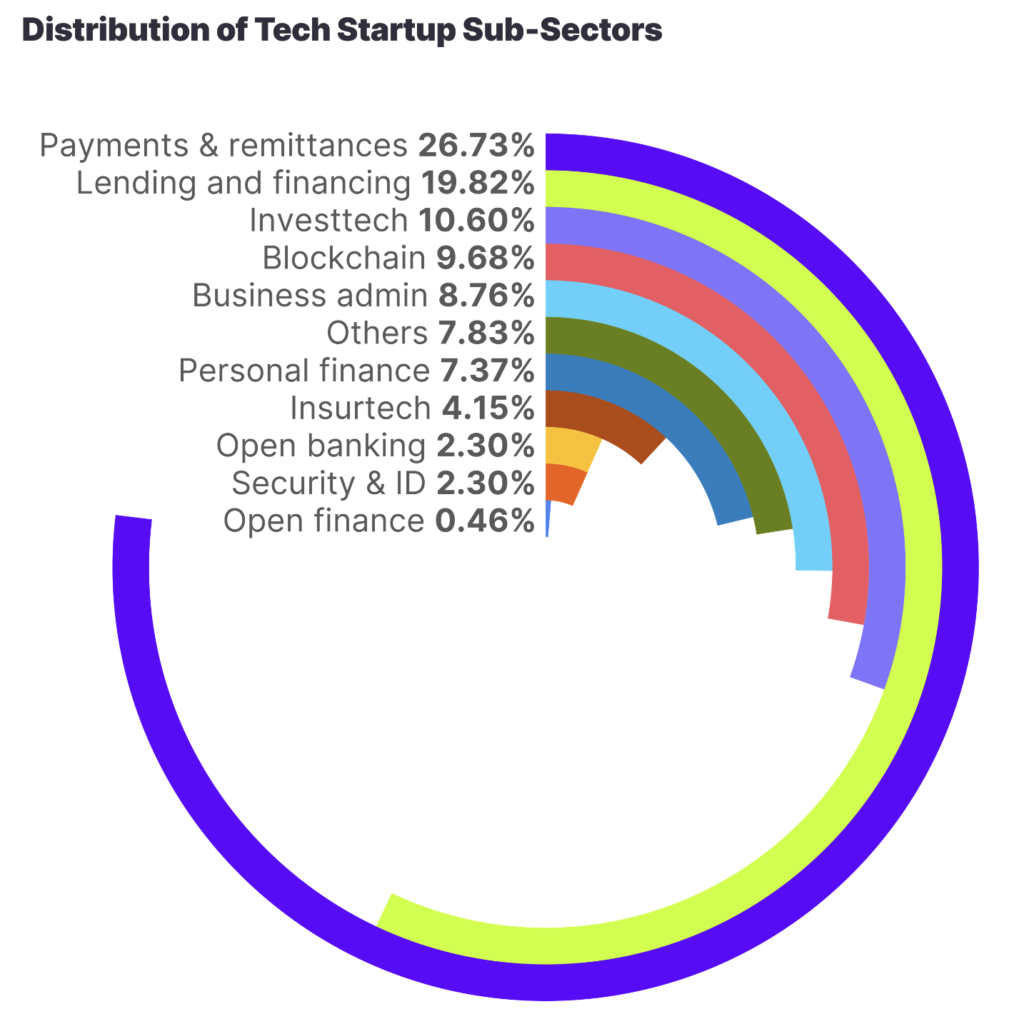
Investment Trends
The investment landscape in Nigeria’s tech ecosystem has become increasingly vibrant. A significant portion of the funding comes from international venture capitalists and angel investors, drawn by the high return potential of Nigerian tech startups. This influx of capital not only validates the market’s potential but also underscores the critical role these businesses play in the country’s economic future.
Economic Impact
The emergence of technology startups in Nigeria has had a tangible impact on the economy, not just in terms of GDP contribution, but also in employment creation and innovation proliferation. Here’s a deeper look at how these startups are driving economic change.
Contribution to GDP
Technology startups are becoming a significant contributor to Nigeria’s GDP. While exact figures vary, it’s estimated that the ICT sector, fueled largely by these startups, contributes about 15% to the GDP as of 2021. This figure has seen a steady increase over the past five years due to the rising number of tech companies and their expanding scope of operations.
Employment Statistics
Tech startups are major employment generators, particularly for the youth. With over 60% of the country’s population under the age of 25, tech startups offer a vital employment outlet, which helps reduce youth unemployment rates. Startups like Andela and Flutterwave have not only created thousands of direct jobs but also foster an ecosystem that supports freelancers and other indirect employment through their platforms.
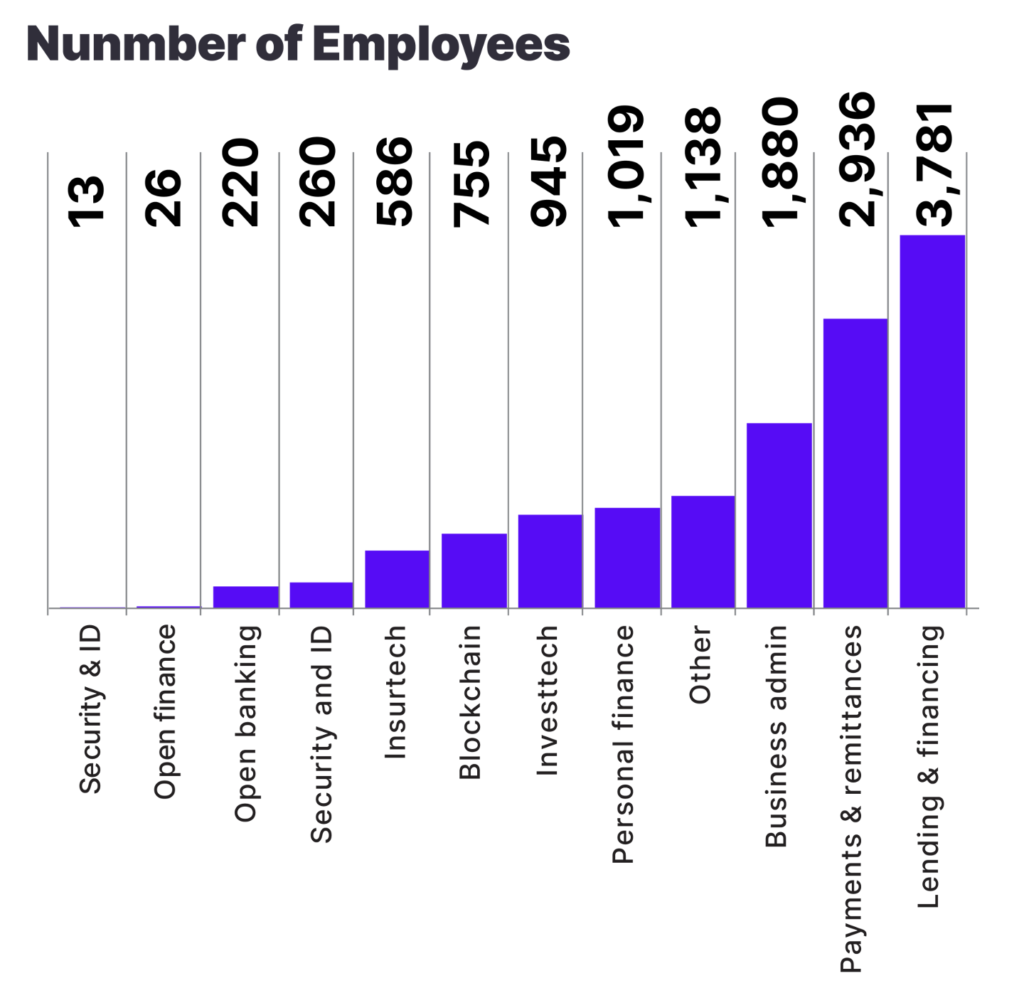
Challenges Facing Tech Startups
Despite their successes, Nigerian tech startups face a variety of challenges that could hinder their potential impact on the economy.
Funding and Investment Issues
While there has been a significant influx of capital, funding remains concentrated in certain sectors like fintech, leaving other potentially transformative sectors underfunded. Additionally, the volatility of global investment markets can impact funding availability.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory landscape in Nigeria can be somewhat unpredictable, with sudden policy changes posing significant risks for startups. For instance, the ban on motorcycle taxis in Lagos impacted many ride-sharing startups adversely.
Infrastructure Limitations
Persistent issues such as unreliable power supply and internet connectivity can severely limit the operations of tech startups. These infrastructure challenges increase operational costs and can stifle the growth and scalability of tech businesses.
The Role of Government and Policy Recommendations
The Nigerian government has taken steps to support the tech ecosystem, such as the establishment of innovation hubs and the offering of grants and tax incentives. However, more targeted actions are required to ensure sustainable growth.
Policy Changes Needed
- Improved Regulatory Frameworks: Clear, stable, and supportive regulations are needed to protect investments and encourage new startups.
Infrastructure Development: Significant investment in improving power and internet services would directly benefit the tech sector.
Education and Training: Enhancing STEM education and entrepreneurial training to supply skilled labor to the growing tech industry.
Future Prospects
The trajectory of Nigeria’s tech startup scene looks promising, with several emerging technologies and market trends expected to drive further growth and innovation. Here’s what the future might hold:
Predictions for the Tech Startup Scene
Continued Growth in Fintech: Given the success of companies like Paystack and Flutterwave, the fintech sector is expected to continue dominating the startup landscape. Innovations in payment systems, mobile money, and financial inclusion are likely to attract further investment.
Expansion into New Sectors: As digital transformation deepens, sectors such as edtech, healthtech, and logistics are set to expand. These sectors will likely leverage technology to solve pressing local issues, such as education access, healthcare delivery, and supply chain management.
Increased Local and International Investment: With proven success stories and a growing market, more local investors are expected to back tech startups, alongside continued interest from international venture capitalists.
Emerging Technologies with Potential for Growth
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML are beginning to play critical roles in customer service, financial services, and health diagnostics in Nigeria. These technologies offer significant potential to personalize services and enhance operational efficiencies.
Blockchain Technology: Beyond fintech, blockchain holds potential for application in securing transactions, real estate, and in establishing transparent supply chains, which could greatly benefit Nigeria’s large agricultural sector.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT technology can be pivotal in transforming urban management, agriculture, and healthcare systems in Nigeria. Smart farming solutions and health monitoring devices are examples of IoT applications that can address local challenges effectively.
Conclusion
The rise of technology startups in Nigeria is a key driver of economic growth, innovation, and employment, particularly among the youth. While challenges such as funding disparities, regulatory uncertainties, and infrastructural deficiencies persist, the overall outlook remains positive. The government’s role in crafting supportive policies and fostering an enabling environment cannot be overstated, as these will be crucial in sustaining the growth trajectory of this vibrant sector.
Nurturing the tech ecosystem in Nigeria is not just about enhancing economic metrics but also about creating a sustainable model of development that leverages technology for societal benefits. As Nigeria continues to position itself as a tech hub in Africa, the strategic importance of supporting this sector will only grow, promising a brighter economic future driven by innovation and entrepreneurship.